Periodontitis — causes, symptoms
and modern treatment methods
What is periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the tissues that hold the tooth within the alveolus: the periodontal ligaments and the surrounding bone structures. Most often, it develops as a complication of dental caries and pulpitis, when the infection penetrates from the root canal into the ligaments and bone. The condition is accompanied by pain, possible suppuration, swelling of the gum, and the risk of cyst formation. In its advanced form, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss.
Types of periodontitis
Infectious periodontitis
Develops due to untreated caries or pulpitis. Bacteria from the pulp spread to the root area and cause inflammation. This is the most common form of the disease.
Traumatic periodontitis
Occurs after trauma to the tooth or jaw, for example after a strong impact or biting a hard object. Microcracks and injuries allow bacteria to enter periodontal tissues.
Medication-induced periodontitis
May occur due to improper treatment of pulpitis or the placement of a non-sealed filling. As a result, food particles and bacteria penetrate deep into the tooth, causing inflammation, which may be accompanied by pulpitis and other complications.
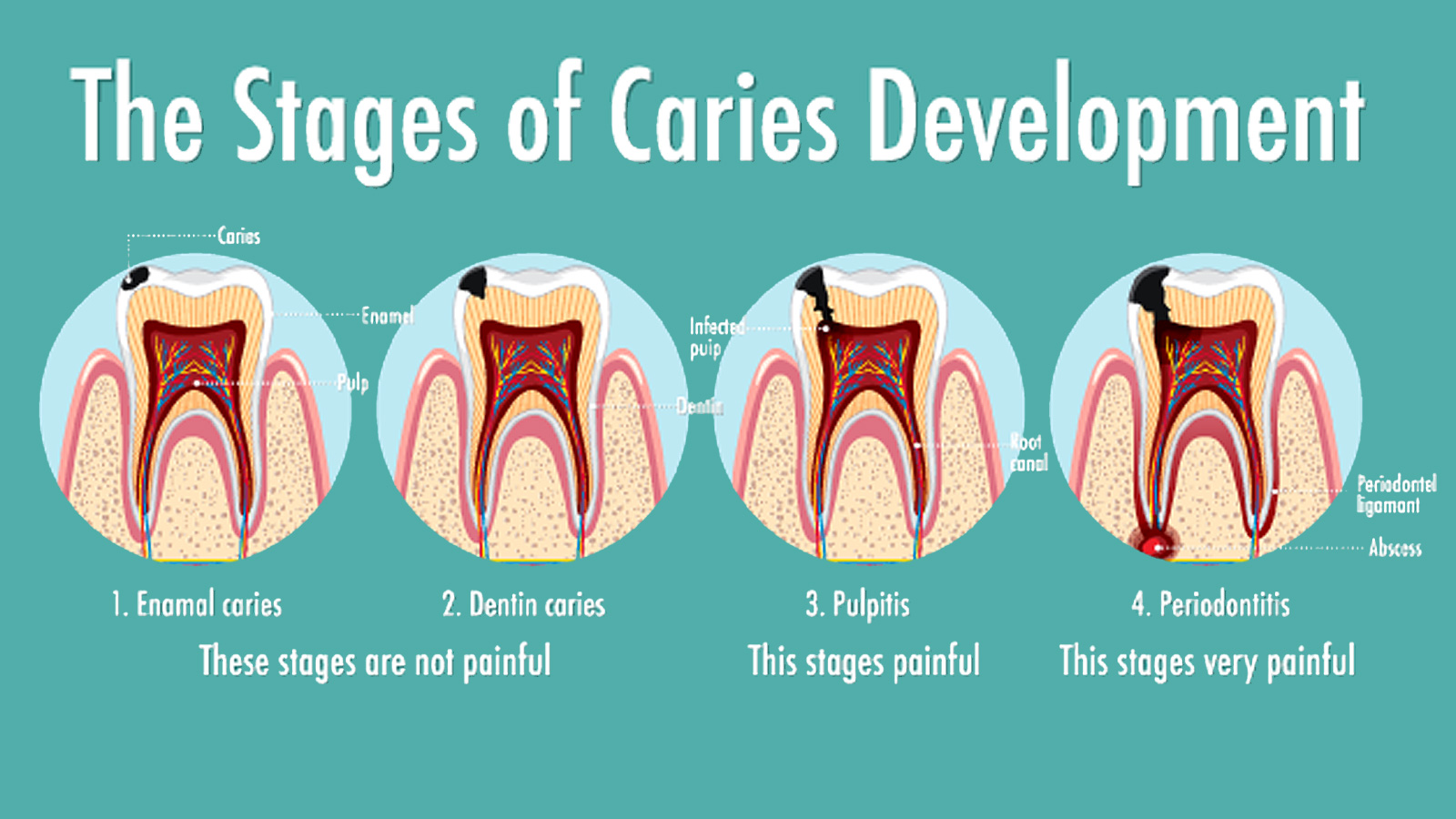
Symptoms of periodontitis
The most characteristic symptom is intense tooth pain that worsens when biting. The pain may radiate to the entire jaw. Swelling and redness of the gum, discharge of pus from the gingival pocket, and fever in acute cases are also common.
Importance of timely treatment
Delaying a visit to the dentist may lead to severe consequences: formation of cysts, destruction of bone tissue, and the need for tooth extraction. Regular examinations and preventive dental visits make it possible to detect the disease early and avoid complications.
Scientific data and statistics
According to the European Federation of Periodontology (EFP), more than 50% of the adult population in Europe experiences various forms of periodontal inflammatory diseases. In Russia, the prevalence of chronic periodontitis among individuals over 30 years old reaches 60–70% (RUDN Journal. Medicine). This confirms the need for systematic prevention and regular professional hygiene.
Prevention of periodontitis
Key preventive measures include proper oral hygiene (brushing teeth at least twice a day, using dental floss and an irrigator), as well as regular visits to the dentist — at least once every six months. Professional procedures such as professional teeth cleaning, fluoride treatment, and ultrasonic tartar removal help reduce the risk of inflammatory conditions.
Treatment of periodontitis at Diplomat Med Center
At Diplomat Med Center, the treatment of periodontitis is performed according to modern protocols. We use digital diagnostics, X-ray imaging, and, if needed, CBCT to accurately identify the inflammation site. Depending on the stage, conservative methods are used (antiseptic treatment, endodontic therapy, administration of medications into the canals) or surgical interventions (cystectomy, root apex resection).
Our team brings together specialists in therapeutic dentistry, gum treatment, and orthodontics, allowing us to create comprehensive plans for restoring oral health. We also offer preventive programs for children and adults, including pediatric dentistry.
Book an appointment for periodontitis treatment at Diplomat Med Center today — we will eliminate inflammation, preserve your teeth, and restore gum health for many years.
