Stomatitis — causes, symptoms, diagnosis
and modern treatment methods at Diplomat Med Center
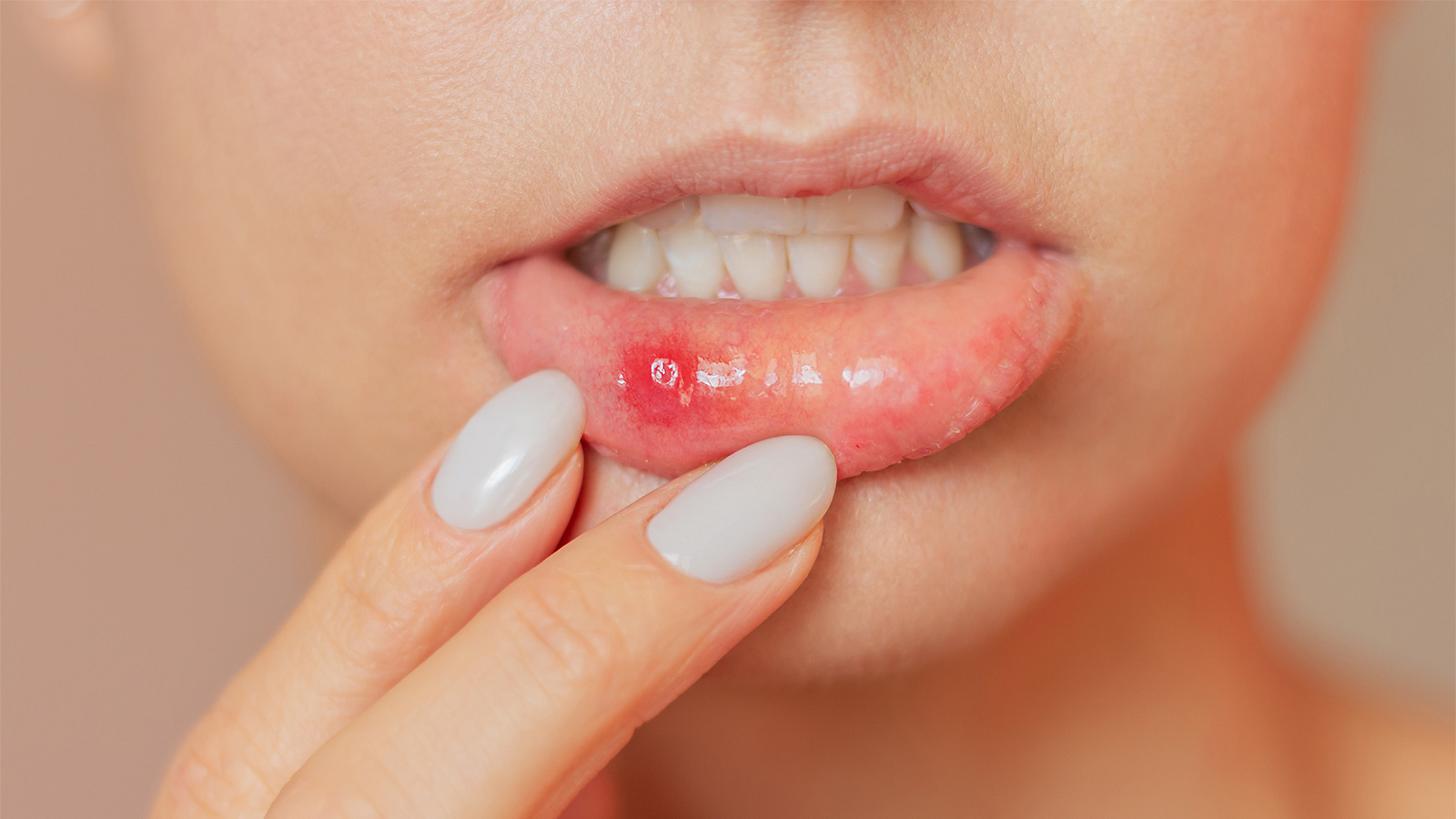
Stomatitis is an inflammatory or ulcerative lesion of the oral mucosa, accompanied by pain, discomfort, and a decrease in quality of life. The condition can occur in patients of any age, although it is indeed more frequently observed in children, which is associated with the characteristics of their immune system and the high prevalence of viral infections. However, modern clinical data confirm that stomatitis is also widespread among adults, especially under conditions of stress, nutritional disorders, smoking, gastrointestinal diseases, weakened immunity, and the use of dental prostheses.
From the perspective of pathogenesis, stomatitis is considered a reaction of the mucous membrane to external (bacterial, viral, fungal, or traumatic) and internal (immune, endocrine, and metabolic) factors. The appearance of whitish plaque, painful vesicles, or aphthae often represents an immune response of the body to damaged epithelial cells. This reaction may be local or associated with systemic disorders.
According to epidemiological data from European population-based studies, recurrent aphthous stomatitis occurs in 5–25% of the population, with the frequency of exacerbations increasing during periods of stress, hormonal fluctuations, and immunodeficiency states (Altenburg et al., Dtsch Arztebl Int., 2009).
In CIS countries, the indicators are similar, and among patients with chronic gastrointestinal diseases, the frequency of recurrences may exceed 30% (data from national clinical registries of therapeutic dentistry, 2022).
Main causes of stomatitis development
The development of stomatitis may be caused by infectious agents, mechanical trauma, impaired salivation, disturbances in the mucosal barrier function, and immune reactions of the body. In adults, one of the most common causes is stress and a reduction in adaptive immunity, which is confirmed by studies published in the Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine (2021): chronic stress increases the risk of exacerbations of recurrent aphthous stomatitis by more than 60%.
Additional predisposing factors include unbalanced nutrition, deficiency of B-group vitamins, iron and folic acid deficiency, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, the presence of dental caries and tartar, as well as mucosal trauma caused by prostheses or orthodontic appliances.
Symptoms and clinical manifestations
The classic signs of stomatitis include whitish plaque on the tongue and inner surface of the cheeks, painful aphthae or vesicles, a burning sensation, and difficulty eating. In more pronounced forms, fever and general weakness may occur, and with candidal stomatitis, a characteristic “cottage cheese–like” coating and unpleasant oral odor may be observed. The specific feature of the disease is that even small ulcers can cause significant discomfort and affect the patient’s quality of life.
It is important to emphasize that attempts to “cauterize” ulcers with alcohol or iodine are strictly contraindicated, as they cause chemical burns and worsen inflammation.
Diagnosis of stomatitis
Diagnosis of stomatitis at Diplomat Med Center aims to determine the form of the disease and the underlying causes. The doctor performs a clinical examination, evaluates the condition of the mucosa, identifies possible traumatic factors, and reviews the history of previous episodes. If necessary, laboratory tests are carried out to detect deficiencies, microbiological analysis, testing for herpetic infection or candidiasis, as well as consultations with a therapist or gastroenterologist in cases of systemic manifestations. This approach allows not only to relieve symptoms but also to eliminate the root cause of the condition.
Modern methods of treatment
Treatment of stomatitis is aimed at reducing inflammation, relieving pain, restoring epithelial tissue, and normalizing the microbial balance of the oral cavity. At Diplomat Med Center, modern therapeutic regimens are used, including local anti-inflammatory and antiseptic medications, prescription gels, rinsing solutions, and in the case of candidal stomatitis — antifungal therapy. In viral stomatitis, antiviral treatment is applied at the prodromal stage, which significantly reduces the duration and severity of symptoms.
Supportive measures include professional oral hygiene (AirFlow, ultrasonic cleaning), correction of restorations and prostheses, elimination of traumatic factors, and personalized recommendations for daily oral care.
Prevention and remission maintenance
To prevent recurrences of stomatitis, it is important to maintain optimal oral hygiene, strengthen immunity, control chronic diseases, and avoid mucosal microtrauma. At Diplomat Med Center, patients receive a personalized preventive care plan, including dietary recommendations and the selection of toothbrushes, toothpaste, and rinsing solutions.
Treatment of stomatitis at Diplomat Med Center
At Diplomat Med Center, treatment is carried out comprehensively — we do not simply relieve pain, but eliminate the causes of the disease and prevent relapses. If necessary, initial treatment includes sanitation of the oral cavity, including caries treatment, restoration of gum health, correction of orthodontic factors (orthodontics), and scheduling of professional dental cleaning.
This approach allows for rapid relief of symptoms, acceleration of healing, and a significant reduction in the frequency of recurrence.
Schedule a consultation at Diplomat Med Center — we will help restore comfort, oral mucosal health, and confidence in your smile.
Diplomat Med Center — with care for your smile.
